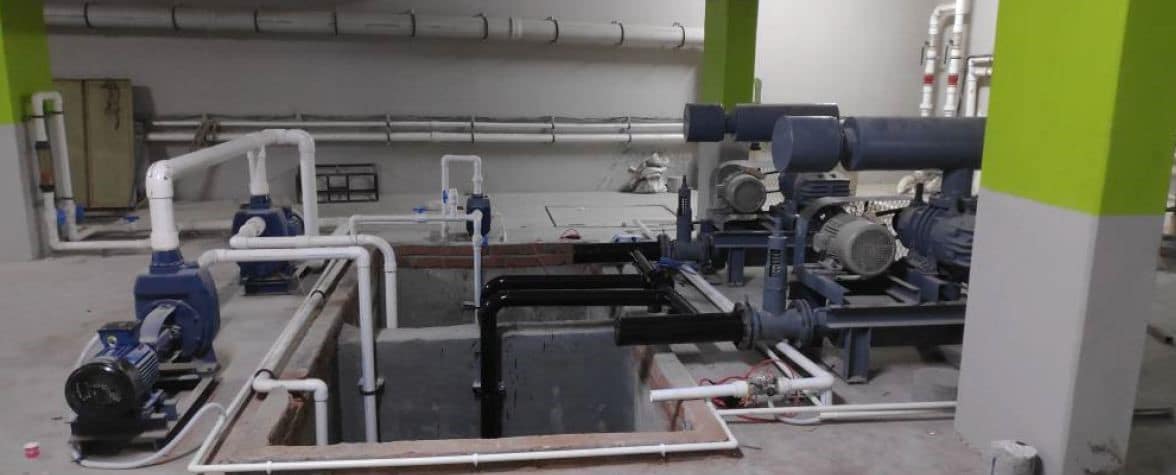
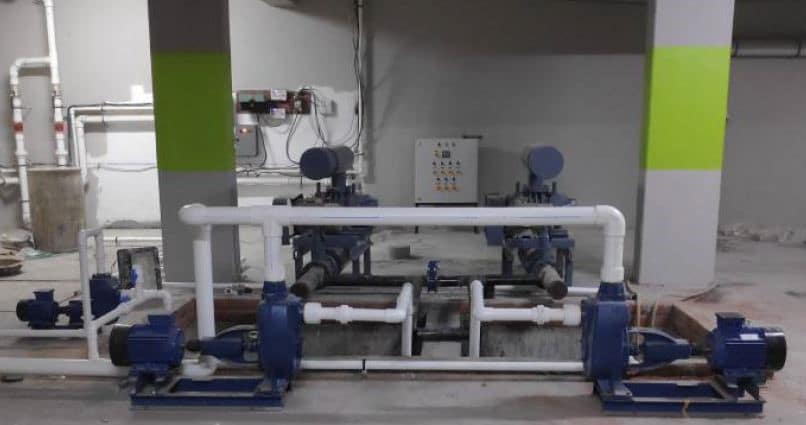
About

Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) is an advanced technology that uses a fill and draws activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. It is best for treating both industrial and municipal wastes. The main difference between SBR technology and other STP technologies is that SBR uses a single batch reactor/single tank to process the equalization, aeration, and clarification compared to other technologies that use different batch reactors for various processes.
Process
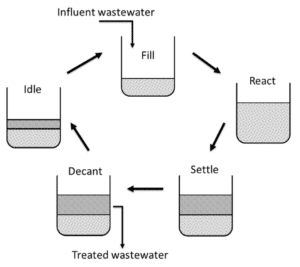
There are four steps involved when using an SBR system:
- Fill cycle– There are two chambers involved in the process, with the wastewater first entering the primary treatment chamber via the inlet. This is where any solid substances will be held before being moved in the secondary chamber.
- Aeration/React cycle– The second batch can now begin, with oxygen introduced into the tank via a diffuser. This is when the biological cleaning process takes place, activating the microorganisms in the waste that will start to clear away the solids.
- Settle phase– Once the aeration cycle has ended, the live sludge will settle at the bottom of the tank, with the clear effluent rising to the top.
- Decant phase– The purified wastewater is then fed into a discharge system via a sampling chamber and out into a drainage field or water course. Once completed, the sludge is then returned from the SBR tank back into the primary treatment chamber.

Applications
- Effluent with a wide range of inflow and/or organic loadings
- Effluent that require minimal operator attention
- Effluent that require extremely close control of effluent quality, such as for removal of nutrients
- Sewage in small to medium size communities
- Effluent in industries with high BOD loadings such as food processing, dairies and chemical plants.
Advantages
- Because SBR technology uses storage and batching system, the effluent can be stored at peak periods and treated in smaller batches throughout the course of any given day. This means each batch is given full treatment time and peak surges are avoided.
- An SBR tank is operated by air power generated by blower/compressor, which means there are no moving parts of electrical components inside the tank itself. This reduces maintenance and replacement costs and makes for a more efficient operation.
- There is no need for final sedimentation tanks or return activated sludge pumping as everything is conducted within a single tank. This also means SBR systems take up a smaller footprint as fewer tanks are required.


